Project number: J4-50130
Principal investitor: dr. Peter Prislan
Overall budget: 300.000,00 EUR
Project duration: 1.11.2023 - 31.10.2026
Partnership: The project is part of a joint project with a foreign team; the ARIS acts as the Lead agency in connection with Czech agency GAČR
ABSTRACT OF THE RESEARCH PROJECT
Climate change, as a combination of warming, changing precipitation patterns and extreme events, has fundamental implications for forests in Central Europe. Future climate conditions may affect forest growth, competitiveness and management practices. However, changing growth conditions may affect not only the productivity of wood but also its structure, properties, and usability. It is uncertain how climate change will affect the availability of wood and how technological advances in the wood-based sector will affect the flow of materials and utilisation of wood. However, based on previous data on climate and wood properties, different models can be developed to assess the availability of wood and its properties under climate change, which can help adapt silvicultural measures.
In recent decades, the timber construction industry has focused mainly on using spruce wood, which is declining in Europe. As a result, supplementary wood species that can cope with increasing drought conditions are needed. Among others, several pine species have been proposed as long-term substitutes. In addition, oak species are very valuable both economically and ecologically. However, relatively little is known about their growth characteristics and wood properties under global warming.
Projections of future wood availability and properties due to climate change are particularly relevant. These changes will also significantly affect the global forest sector regarding wood supply, demand, and production. The main challenge is ensuring productivity (including carbon sequestration) per forest area and restoring forest ecosystem stability, which has declined dramatically in recent years. The main objective of the project proposal is to evaluate the effects of changing environmental conditions on productivity, but also on structural, physical and mechanical properties of pine and oak species adapted to temperate (i.e. Pinus sylvestris L. and Quercus robur L.) and sub-Mediterranean growing conditions (i.e. Pinus nigra J. F. Arnold and Quercus pubescens Willd.) at different sites in Slovenia and the Czech Republic.
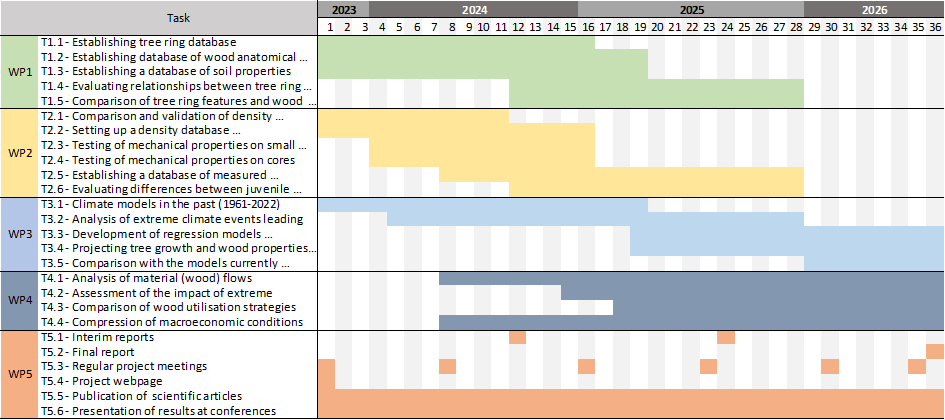
The project proposal is divided into five work packages (WP) that address the specific research questions. The main objective of WP1 is to evaluate the effects of site conditions (weather and soil variables) on radial growth and anatomical features of pine and oak wood between and within selected sites in Slovenia and the Czech Republic. In WP2, physical (density) and mechanical properties (compressive and bending strength and modulus of elasticity) will be analysed at the same sites as in WP1. The first two work packages will also evaluate the differences between juvenile and adult wood. The databases created in WP1 and WP2 will be used in WP3 to evaluate the relationships between tree ring characteristics, wood anatomy, wood properties, and environmental variables (e.g., temperature, precipitation, vapour pressure deficit). The models created will be used to predict wood properties in response to climate change scenarios at the country level. In WP4, the impact of changes in the availability of wood and its properties on the bioeconomy will be assessed. The focus will be on comparing material flow balances (wood) between countries in normal years and in years affected by extreme weather events. In WP5, tasks and activities related to communication and dissemination of results are foreseen.
The research design, with the north-south gradient in combination with selected species adapted to different growing conditions, will make it possible to evaluate the performance of the selected species under climate change at Slovenian and Czech sites. Established models explaining the relationships between environmental factors, wood structure, and wood properties can be used to predict responses to climate change scenarios. Such information is critical for predicting wood availability and flows in the forest-based bioeconomy.
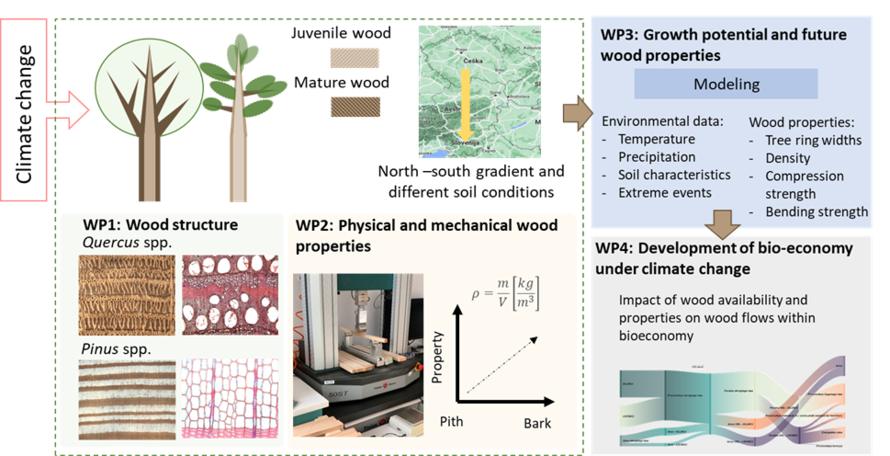 Scheme of the research idea and project goals within work packages (WPs). Climate change will affect the growth of trees (at sites with different soil conditions) and thus forest productivity, wood structure (WP1), and its physical and mechanical properties (WP2). Models explaining the relationships between environmental factors and wood properties (WP3) can be used for strategic
analyses of potential wood resources and for planning improvements in the wood flow to industrial plants (WP4).
Scheme of the research idea and project goals within work packages (WPs). Climate change will affect the growth of trees (at sites with different soil conditions) and thus forest productivity, wood structure (WP1), and its physical and mechanical properties (WP2). Models explaining the relationships between environmental factors and wood properties (WP3) can be used for strategic
analyses of potential wood resources and for planning improvements in the wood flow to industrial plants (WP4).
Project timeline